Bitumen Tests Explained: Softening, Ductility & Flash Point
Table of Contents
Bitumen Tests Explained: Softening, Ductility & Flash Point, Bitumen Tests in Highway Engineering: Softening Point, Ductility, Flash & Fire Point Explained
BITUMEN
- obtained by fractional distillation of crude oil.
- soluble in carbon tetra chloride & carbon disulphide.
- less resistance to temp.
- more resistance to weathering.
- less resistance to temp.
- used for damp proof course.
TAR
- obtained by destructive distillation of coal & wood.
- soluble in toluene.
- more resistance to temperature.
- less resistance to weathering.
- more resistance to temp.
- used for coating a wooden frame.
- RT-1 – lowest viscosity → for surface painting
- RT-4 – premix in macadam.
- RT-5 – grouting (highest viscosity)
Form of Bitumen
1) Cutback bitumen
- obtained by reducing the viscosity of bitumen wit/’;h diluents (volatile).
- It is used in colder regions.
- Cutbacks are designated by numerals representing viscous cutback.
e.g. RC-2 is more thick than RC-1 but RC-1, MC-2, SC-2 have same viscosity.
(1) Slow curing cutback (SC)
- obtained by blending with high-boiling-point gas oil. (naphtha or gasoline oil).
(2) Medium curing cutback
- They have good wetting properties.
- Bitumen is flux with kerosene, light diesel oil.
(3) Rapid curing cutback
- They have penetration value of 80 to 120.
- flux with naphtha or gasoline oil.
2) Emulsion bitumen
- It is two-phase system consisting of two immiscible liquids.
- It is used rainy season.
- Emulsion can be used for soil stabilization in desserts.
- Bitumen/tar content in emulsion range for 40% to 60%, and remaining portion is water.
• Emulsion bitumen
- Slow setting bitumen – used for surface dressing work.
- Medium setting bitumen – used for patch up work.
- Rapid setting bitumen –
TEST ON BITUMEN
1) Penetration test
- Determines the hardness indirectly.
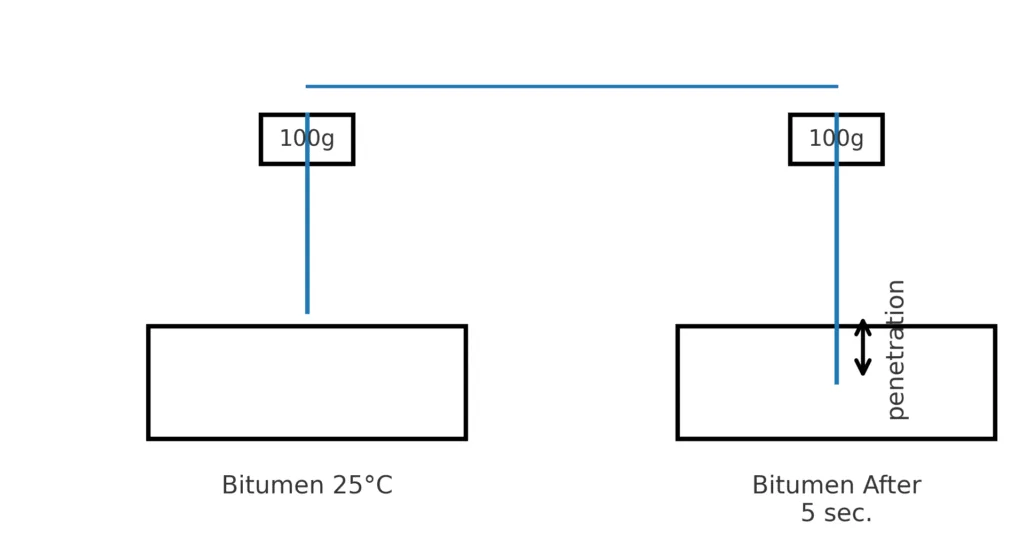
- Unit of penetration is 1/10 mm
- Load = 100g
- Penetration value ↑ → Hardness ↓
- Example: 80/100 means penetration of 8–10 mm.
- Common grades are 80/40, 60/10 & 80/100.
- Tars are soft, so a penetration test is not used.
2) Solubility
- It is used to measure the quantity of impurity in bitumen with the help of CS₂ and CCl₄.
- Solubility of bitumen in trichloroethylene is a measure of its purity.
- As per IRC, insoluble material should not be greater than 1%.
3) Ductility test
- It is a measure of the elasticity of the material.
- It should be capable of being stretched without breaking.
- Stretching standard briquette having c/s area 1 sq. cm at 27°C at a rate of pull being 5 cm/min → 50 mm/min.
As per ISI, the minimum value of ductility is 75 cm.
4) Spot test
- This test is used to determine overheated or cracked bitumen.
- More sensitivity than the solubility test for the detection of cracking.
- 2 gm of bitumen is mixed with 10 ml of naphthalene, and the solution is prepared & placed in a filter paper.
- Stain spot → uniform colour → uncracked bitumen
- Stain → annular ring thick, brown or black at centre & fair at periphery → overheated or cracked bitumen
5) Viscosity of bitumen (cup viscometer)
- The property of bitumen which resists the flow due to internal friction.
- Viscosity of liquid bitumen measured by efflux viscometer.
- Methods used are STV (Standard Tar Viscometer), Saybolt, Furol, Redwood & Engler.
- Furol viscosity is a standardised test.
- In this test, the time taken is in seconds at the given temperature. 60°C.
- When the time taken is more, the viscosity of bitumen is higher.
- More viscosity → less compaction
6) Softening point
- Measured by the ring & ball apparatus.
- Softening point is the temperature at which bitumen attains a particular degree of softness.
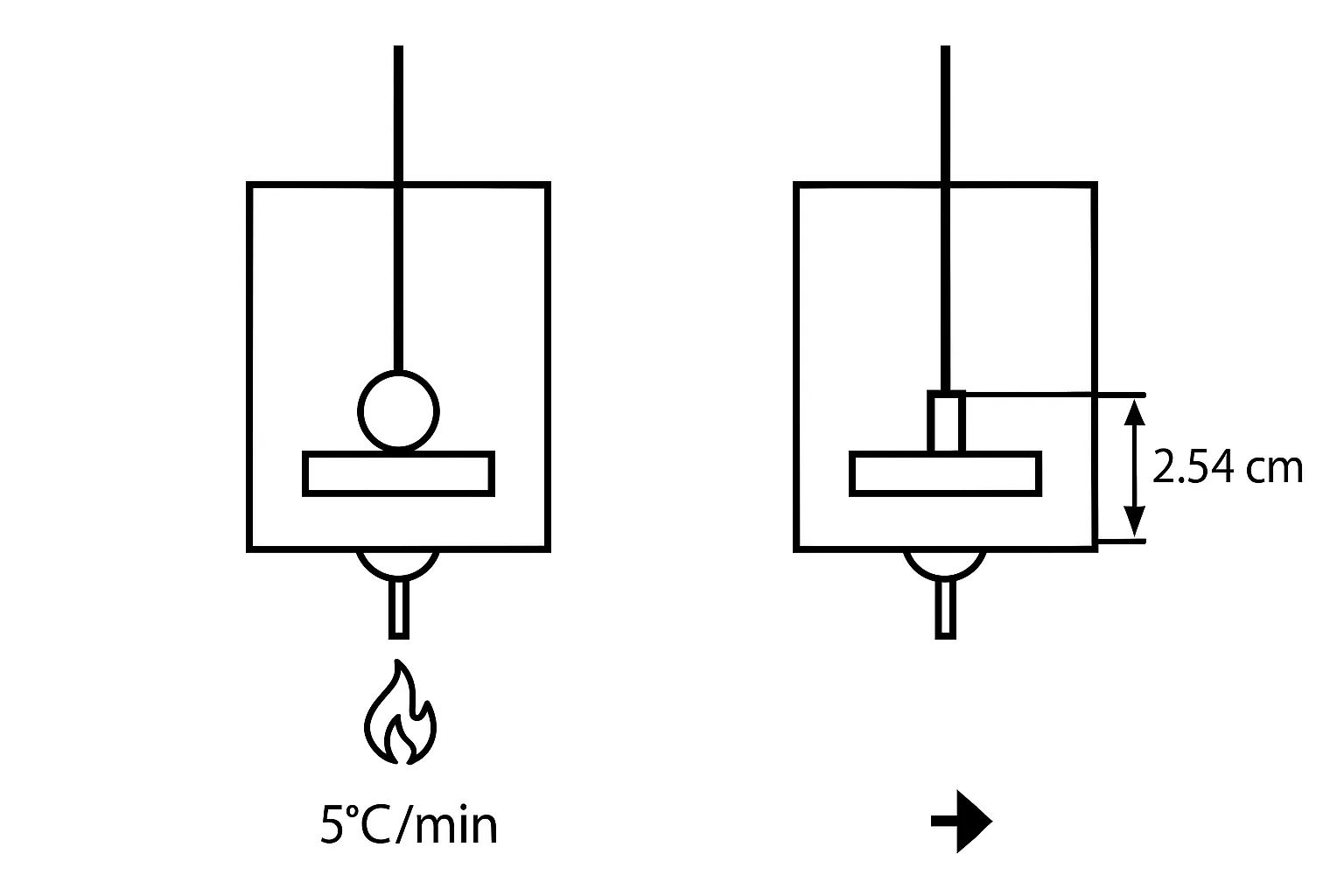
- More softening point = the material is more harder.
- Softening point ⇒ 35°C to 70°C
7) Flash & Fire point
- Flash point – Flash point of a material is the lowest temperature at which vapours take fire in the form of a flash.
- Fire point – Temperature at which the material gets burnt (burns for 5 sec at least).
- In this test, the apparatus used is Pensky–Marten’s close cup apparatus.
- Flash point ⇒ 175°C (specified by IRC).
- Safe limit for heating bitumen is normally 50°C below the flash point.
8) Specific Gravity
- Determined by the pycnometer method.
- Measurements are taken at 27°C. The specific gravity is generally 1.0.
- Bitumen ⇒ 0.97 – 1.02
- Tar ⇒ 1.10 – 1.25
9) Water Content Method
- Maximum water content in bitumen should not exceed 0.2% by weight.
Bitumen Tests Explained: Softening, Ductility & Flash Point
- History of Road Construction and Highway Planning in India: – https://engineerlatest.com/history-of-road-construction-and-highway-planning-in-india/
- Rail Joints in Railways: Types, Applications, and Importance:- https://engineerlatest.com/rail-joints-in-railways-types-applications-and-importance/










1 comment