Calculation of Base & Storey Shear
Table of Contents
Calculation of Base & Storey Shear
Design Data
- Column = 400 × 400 mm
- L/D Ratio = 70
- X-Direction Beam = B=230×500 mm
- Y-Direction Beam = B=280×750 mm
Project Location
- Bengaluru, Zone-II
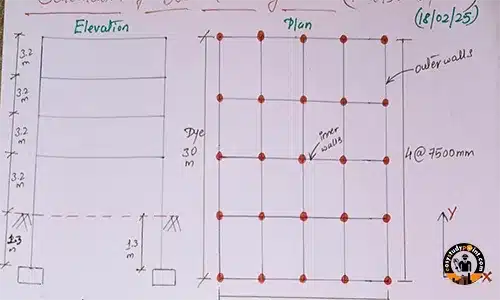
- No. of Floors = 8+G+38 + G + 38+G+3 (Floors) = (4 slabs)
Building Dimensions
Building height is less than 15m, EQM can be used!
- Height of the Building = H=14.1H
- Width of the Building = W=20 m (DxL))
- Length of the Building = L=30 m (Dye)
Wall Details
- Outer Walls = t=230 mm
- Inner Walls = t=150 mm
- Density = 20 kN/m^3
Time Period Calculation (Equivalent Static Method)
T_a = \frac{0.09 h}{\sqrt{d}} ,
T_{ay} = \frac{0.09 \times 14.1}{\sqrt{30}} = 0.231 \text{ sec}Spectral Acceleration, S_a/g
\frac{S_a}{g} ,
T_{ax} = 2.5 \text{s}, \quad T_{oy} = 2.5Refer IS 1893:2016 Cl.no 6.4.2 pg no – 9
For medium stiffness soil sites (0<T<0.55s)
Base Shear Calculation, Vb
V_B = A_h \cdot Wwhere,
( V_B ) = Base Shear,
( A_h ) = Horizontal Acceleration Coefficient,
( W ) = Seismic Weight
Z = 0.10 – Refer to Table 3 pg no.10
I = 1.2- Refer Table 8 Cl.no 7.2.3 pg no – 19
R = 5 – Refer to Table 9 Cl.no 7.2.6 pg no – 20 (RC buildings with SMRF)
A_h = \left( \frac{0.10}{2} \right) \times \left( \frac{1.2}{5} \right) \times 2.5 = 0.03 (Max. horizontal acceleration coefficient)
Seismic Weight Calculation (175mm THK Slab)
Slab area/floor:
x=20+0.2+0.2=20.4m
y=30+0.2+0.2=30.4my
Area=20.4×30.4=620.16≈621m2
1) Self-weight of slab per floor
= 25 kN/m3×(621×0.175)m3 =2716.88 kN
2) Floor Finish Load per floor
=1.5 kN/m2×(621)m3
=931.5 kN
3) Live Load (3 kN/m²) (Reduced L.L)
= 0.25×3 kN/m2×(621)m2
=465.75≈466 kN
Total Load
=1115 kN/floor
(Refer IS 1893:2016 Table-10 Cl. 7.3.1 pg no – 20)
Beam weight calculation
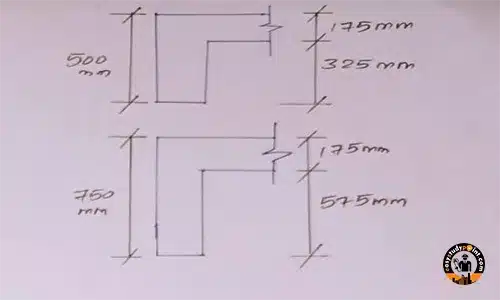
Self-weight of beam
= 25 kN/m³ × (0.325 × 0.225 × 0.4) × 5
= 0.3
(Along x-beam)
(0.55 × 3.0 × 1.5)
(Along y-beam)
= 25 kN/m³ × (33.15 + 87.4) m³
= 25 × 0.3 × (3.15 + 8.94)
= 904 + 125
= 905 kN/floor
Masonry wall calculation
Outer wall load (20% opening/storey)
Self-weight of outer walls =
= 20 kN/m³ × 0.23 × 0.8 ×{(3.2 – 0.5) × 20.4 × 2 + (3.2 – 0.25) × 30.4 × 2}
(Along x-axis) (Along y-axis)
= 20 × 0.23 × 0.8 × (10.16 + 148.92)
= 20 × 0.23 × 0.8 × 259.12
= 953.56
≈ 954 kN
Inner wall load (20% opening/storey)
Self-weight of inner wall =
= 20 kN/m³ × 0.115 × 0.8 ×{(3.2 – 0.5) × 20.4 × 3 + (3.2 – 0.25) × 30.4 × 3}
(Along x-axis) (Along y-axis)
= 20 × 0.115 × 0.8 × (165.24 + 223.44)
= 715.17 kN
≈ 716 kN
Total weight of wall/storey = 954 + 716 = 1670 kN

- Self-weight in GL/1st storey
- [/latex] \frac{1670}{2} = 835 \text{ kN} </li> </ul> </li><li><strong>Self-weight in the 2nd storey</strong> <ul class="wp-block-list"> <li> \frac{1670 + 1670}{2} = 1670 \text{ kN} [/latex]
- Self-weight in the 3rd storey
- \frac{1670 + 1670}{2} = 1670 \text{ kN}
- Self-weight in the 4th storey
- \frac{1670}{2} = 835 \text{ kN}
Column weight calculation
- Self-weight of all 30 columns (GL/1st storey)
- = 25{ kN/m}^3 \times 0.4 \times 0.4 \times \left( \frac{4.5}{2} + \frac{3.2}{2} \right) \times 25
= 25 \times 0.4 \times 0.4 \times 96.25
=385kN
- = 25{ kN/m}^3 \times 0.4 \times 0.4 \times \left( \frac{4.5}{2} + \frac{3.2}{2} \right) \times 25
- Self-weight of all columns in the 2nd storey
- = 25{ kN/m}^3 \times 0.4 \times 0.4 \times \left( \frac{3.2}{2} + \frac{3.2}{2} \right) \times 25
= 320kN
- = 25{ kN/m}^3 \times 0.4 \times 0.4 \times \left( \frac{3.2}{2} + \frac{3.2}{2} \right) \times 25
- Self-weight of all columns in the 3rd storey
- = 25 \text{ kN/m}^3 \times 0.4 \times 0.4 \times \left( \frac{3.2}{2} + \frac{3.2}{2} \right) \times 25
=320kN
- = 25 \text{ kN/m}^3 \times 0.4 \times 0.4 \times \left( \frac{3.2}{2} + \frac{3.2}{2} \right) \times 25
- Self-weight of all columns in the 4th storey
- =25 \text{ kN/m}^3 \times 0.4 \times 0.4 \times \left( \frac{3.2}{2} \right) \times 25
=160kN
- =25 \text{ kN/m}^3 \times 0.4 \times 0.4 \times \left( \frac{3.2}{2} \right) \times 25
Seismic weight calculation per storey
Seismic weight = Slab load + Beam load + Wall load + \frac{\text{Column load}}{\text{floor}}
- Seismic weight of the Ground storey-
= W1 = 4115 + 905 + 835 + 385
= 6240kN - Seismic weight of the 2nd storey
= W2 = 4115 + 905 + 1670 + 320
= 7010kN - Seismic weight of 3rd storey
=W3 = 4115 + 905 + 1670 + 320
=7010kN - Seismic weight of 4th storey
=W4 = 4115 + 905 + 835 + 160
= 6015kN
Total seismic weight (W)= W = W1 + W2 + W3 + W4
= 6240 + 7010 + 7010 + 6015
= 26275 kN
V_B = Ah x w
V_B = 0.03 x 26275 =78.25kN
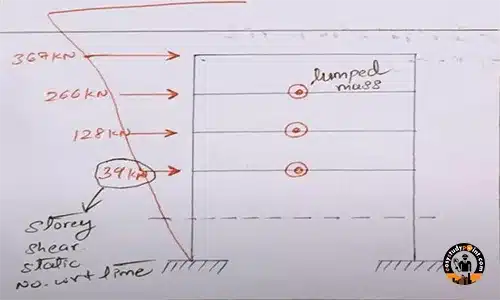
(Distribute this base shear to every storey/floor level)
Storey Shear Calculation: (Q)
h1 = 4.5m,
h2 = 4.5 + 3.2 = 7.7m
h3 = 7.7 + 3.2 = 10.9m,
h4 = 10.9 + 3.2 = 14.1m
Design Lateral Force (Q)
Q_i = \frac{W_i h_i^2}{\sum\limits_{j=1}^{n} W_j h_j^2} \times V_B , (Refer IS1893:2016 part 1 Pgno.23)
Q_1 = \frac{W_1 h_1^2}{W_1 h_1^2 + W_2 h_2^2 + W_3 h_3^2 + W_4 h_4^2} \times V_B Q_1 = \frac{(6240 \times 4.5^2) + (7010 \times 7.7^2) + (7010 \times 10.9^2) + (6015 \times 14.1^2)}{126360 + 415622.9 + 832858.1 + 1195842} \times 788.25 Q_1 = \frac{126360}{126360 + 415622.9 + 832858.1 + 1195842} \times 788.25Q_1 = 38.74 kN
Q_2 = \frac{W_2 h_2^2}{W_1 h_1^2 + W_2 h_2^2 + W_3 h_3^2 + W_4 h_4^2} \times V_B Q_2 = \frac{7010 \times 7.7^2}{(6240 \times 4.5^2) + (7010 \times 7.7^2) + (7010 \times 10.9^2) + (6015 \times 14.1^2)} \times 788.25Q2= 127.44kN
Q_3 = \frac{W_3 h_3^2}{W_1 h_1^2 + W_2 h_2^2 + W_3 h_3^2 + W_4 h_4^2} \times V_B Q_3 = \frac{7010 \times 10.9^2}{(6240 \times 4.5^2) + (7010 \times 7.7^2) + (7010 \times 10.9^2) + (6015 \times 14.1^2)} \times 788.25Q3= 255.38kN
Q_4 = \frac{W_4 h_4^2}{W_1 h_1^2 + W_2 h_2^2 + W_3 h_3^2 + W_4 h_4^2} \times V_BQ4 = 366.68
Recommended Books:-
1. “Dynamics of Structures: Theory and Applications to Earthquake Engineering” – https://amzn.to/41GhwPU
2. “Earthquake Resistant Design of Structures”- https://amzn.to/3F5jbWn
3. “Structural Dynamics: Theory and Computation” – https://amzn.to/3XlVvTN
4. Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete and Masonry Buildings – https://amzn.to/3Dt7PLj
Also read:- Staircase Basics, Design, Components, Types, and Safety Standards










1 comment