Differences Between IS 1893:2016 and IS 1893:2025 for Earthquake Resistant Design
Table of Contents
Differences Between IS 1893:2016 and IS 1893:2025 for Earthquake Resistant Design
Overall Structure of the Code:
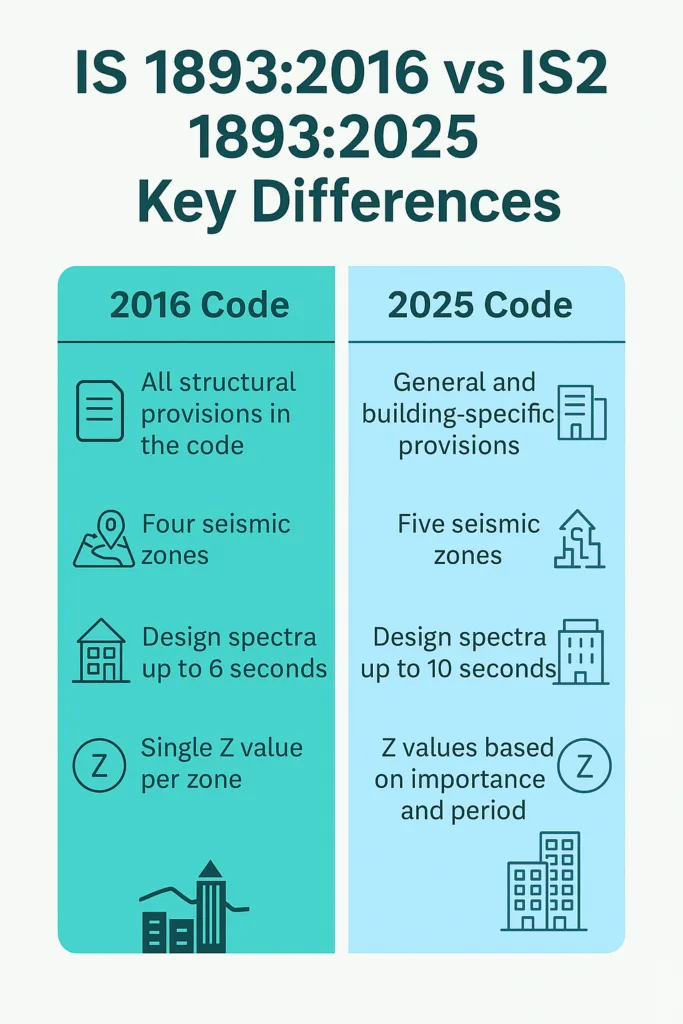
The 2016 version combined all structural provisions into a single code. In the 2025 version, the code splits into general provisions and building-specific provisions. This means designers need to follow different parts of the code depending on the structural type, which helps in applying the right level of detail.
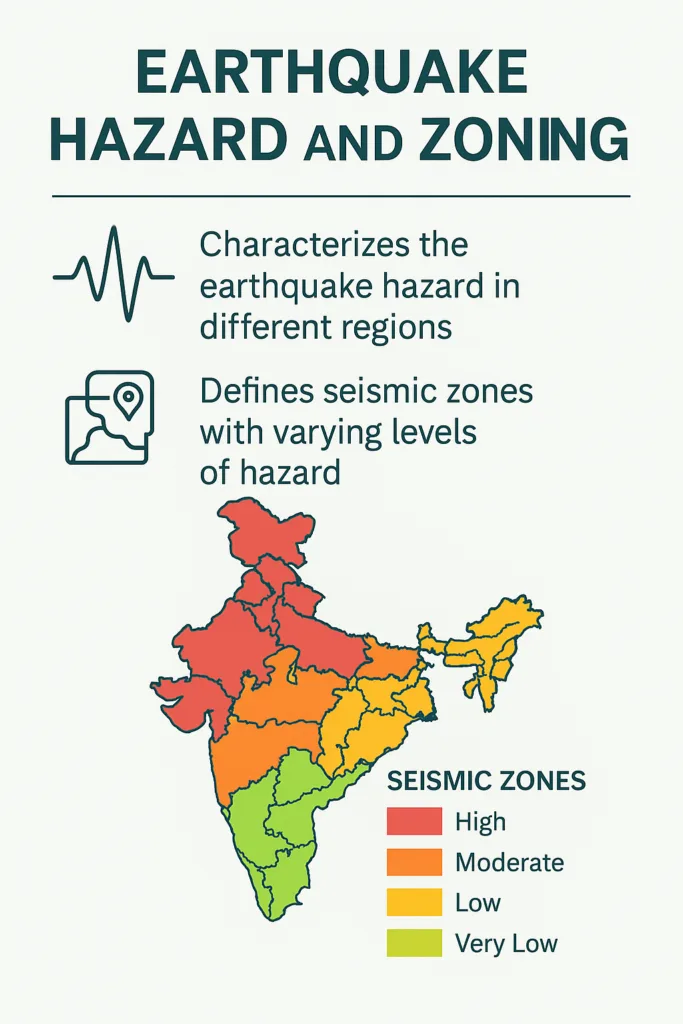
Earthquake Hazard and Zoning:
Previously, we had four seismic zones. The new code introduces five zones, adding more granularity. The zoning is now based on probabilistic seismic hazard assessments, which use more realistic data like recurrence intervals and local geotechnical conditions. This means design is more tailored to local seismic realities.
Design Spectra:
The 2016 code defined the horizontal spectral values up to 6 seconds. In 2025, this is extended to 10 seconds to account for taller structures and long-span bridges, ensuring more accurate design for tall buildings.
Design PGA (Z-Values):
In the old code, there was a single Z value per zone. The new code adjusts Z values based on building importance categories and seismic periods, meaning critical infrastructure like hospitals will have higher design standards.
Soil-Structure Interaction (SSI)
The 2016 code had only basic guidance on SSI. The new version introduces more detailed methods to account for soil flexibility and damping, leading to more realistic structural responses.
Dynamic Analysis
The new code requires more rigorous time history analyses for certain zones, making earthquake modeling more accurate but also a bit more complex.
Why was IS 1893:2025 introduced
The new code was introduced to incorporate the latest research and advancements in seismic hazard assessment and to improve the overall safety of structures in earthquake-prone areas.
Who needs to comply with IS 1893:2025?
Structural engineers, architects, builders, and local authorities responsible for building codes in seismic zones should all ensure compliance with the new code.
How does IS 1893:2025 differ most from the 2016 version?
One of the biggest differences is the shift to a more probabilistic seismic hazard assessment, as well as updates to seismic zoning and design spectra.
Why IS 1893:2025 is Important
The introduction of IS 1893:2025 marks a significant step forward in the field of earthquake-resistant design. This updated code reflects the latest understanding of seismic risks and incorporates new research and methodologies. By adopting IS 1893:2025, engineers and builders can design structures that are better equipped to withstand earthquakes, ultimately enhancing the safety and resilience of buildings in seismic zones.
Who Should Follow IS 1893:2025?
The updated code is essential for a wide range of professionals in the construction and engineering industries. Structural engineers, architects, and builders working in earthquake-prone areas should familiarize themselves with the new requirements. Additionally, policymakers and local authorities responsible for building regulations will also need to adopt these standards to ensure compliance and public safety. By following IS 1893:2025, all stakeholders contribute to creating a safer built environment.
Differences Between IS 1893:2016 and IS 1893:2025 for Earthquake Resistant Design
- Creep of Concrete: Definition, Mechanisms, Effects & Long-Term Deflection Explained:- https://engineerlatest.com/creep-of-concrete-explained/#google_vignette
- Shrinkage in Concrete: Types, Causes, Effects & Design Considerations Explained:- https://engineerlatest.com/shrinkage-in-concrete-types-effects-design/
- The Arch bridges and Cantilever Bridges:- https://engineerlatest.com/the-arch-bridges-and-cantilever-bridges/
- Steel Bridges Types and Benefits:- https://engineerlatest.com/steel-bridges-types-and-benefits/
- Truss Bridges, Types, Design Benefits, and Components Overview:- https://engineerlatest.com/truss-bridges-types-design-benefits-and-components-overview/
- Footings and Foundations Explained: Types, Functions, and IS 456 Guidelines:- https://engineerlatest.com/footings-and-foundations-explained/
- Back Stay Analysis in Tall Buildings | Direct vs Indirect Lateral Load Path Explained:- https://engineerlatest.com/back-stay-analysis-in-tall-buildings-direct-vs-indirect-lateral-load-path-explained/









Post Comment