Important Surveying, Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Concepts for Civil Engineers
Table of Contents
Important Surveying, Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Concepts (Explained Simply)
Surveying and remote sensing are core subjects in civil engineering. Many students struggle because concepts are often written in short exam-oriented notes. In this article, I’ve explained key concepts in simple language, with clear meaning and proper structure, making it useful for students, exams, and professionals.
Basic Surveying Concepts
Versine of a Curve
The versine of a curve is defined as the mid-ordinate of a curve. It is the vertical distance between the midpoint of a chord and the arc of the curve.
Additive Constant
An additive constant is a fixed correction added to measured values to obtain accurate results. It is commonly used in distance measurement instruments.
Deflection Angle
The deflection angle is the angle between the extension of a straight line and the next line in a traverse or curve.
Height and Distance Relationship
When both the height of the observer and the height of the object are given, the distance between them can be calculated using standard surveying formulas.
Weighted Mean
When combining measurements of different reliability, the weighted mean is used instead of a simple average.
Greater weight is given to more reliable observations.
Remote Sensing and Photogrammetry
Radiometer
A radiometer is a passive remote sensing instrument. It does not generate its own energy but records naturally reflected or emitted radiation.
Probable Error
The probable error of a line is calculated by combining the errors in its components. It helps in understanding the accuracy of measurements.
Degree of Accuracy in Levelling
The degree of accuracy in levelling is expressed as:
Error of closure ÷ √(Horizontal length of route)
This formula indicates how precise the levelling work is.
Photogrammetry Basics
Length by Tie-Line Points
In photogrammetry, lengths can be computed using tie-line points having different elevations but known positions on the ground and the photograph.
Important Photogrammetry Terms
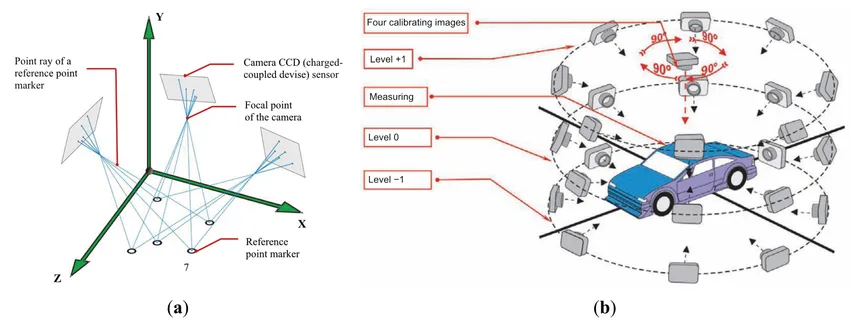
- Isocentre: Point where the bisector of the tilt angle meets the photograph
- Nadir Point: Point where the plumb line from the camera lens intersects the photograph
- Principal Point: Point where the perpendicular from the front nodal point meets the photograph
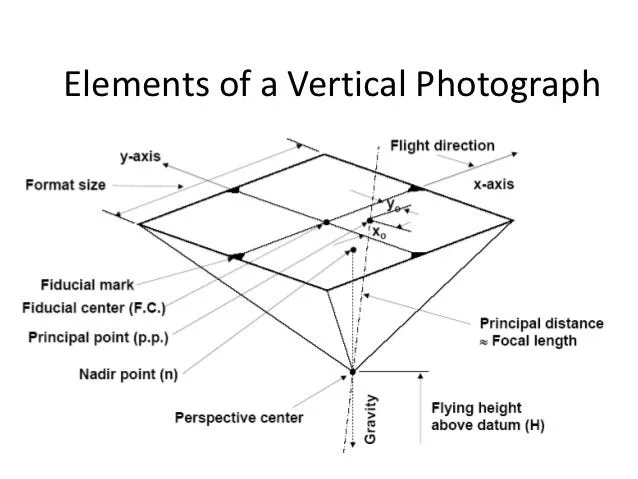
These points help in understanding camera orientation and image geometry.
Passive and Active Remote Sensing Systems
Passive System
A passive system uses naturally available energy (like sunlight).
Examples:
- Photographic cameras
- TV cameras
- Radiometers
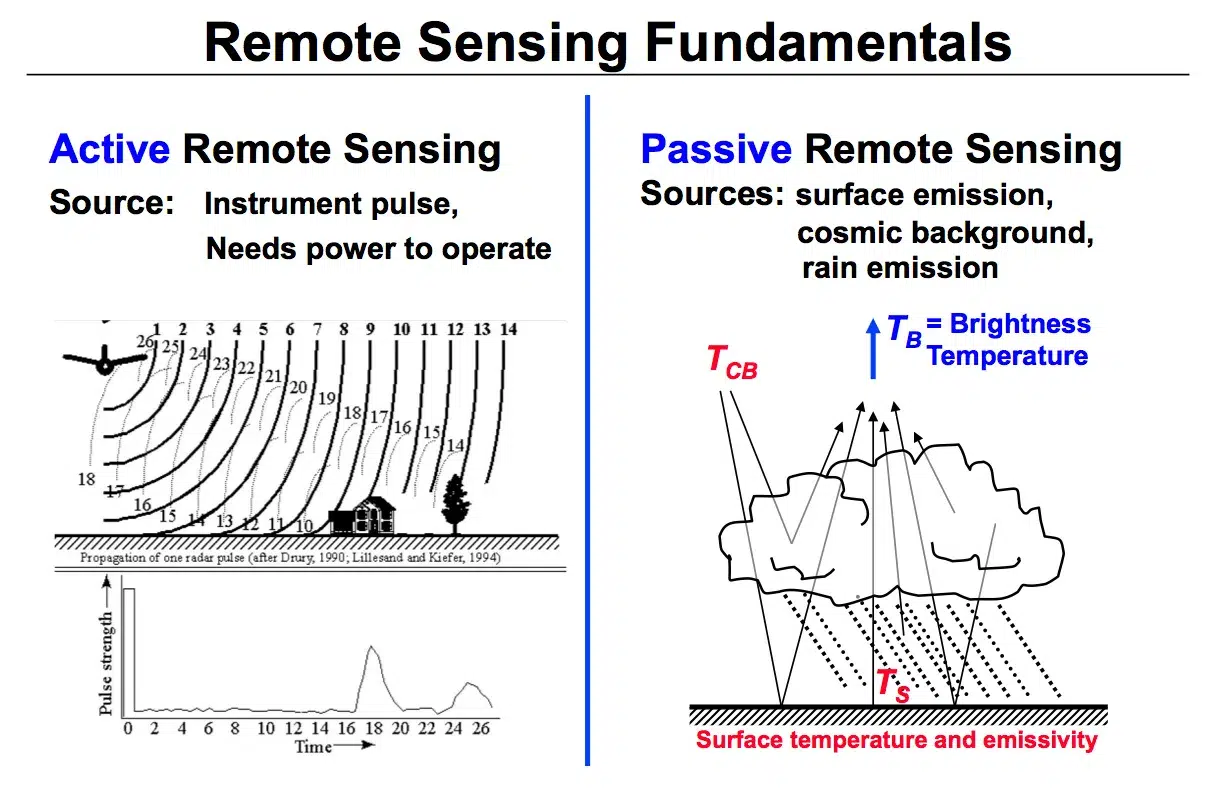
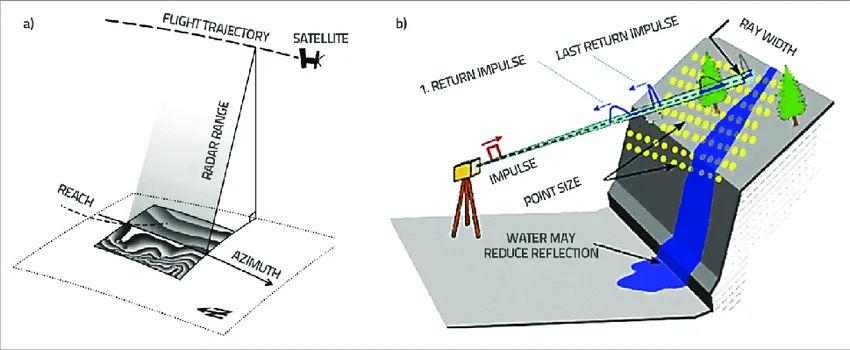
Active System
An active system uses a man-made energy source to collect data.
Examples:
- RADAR
- LiDAR
- Laser scanners
Resolution in Remote Sensing
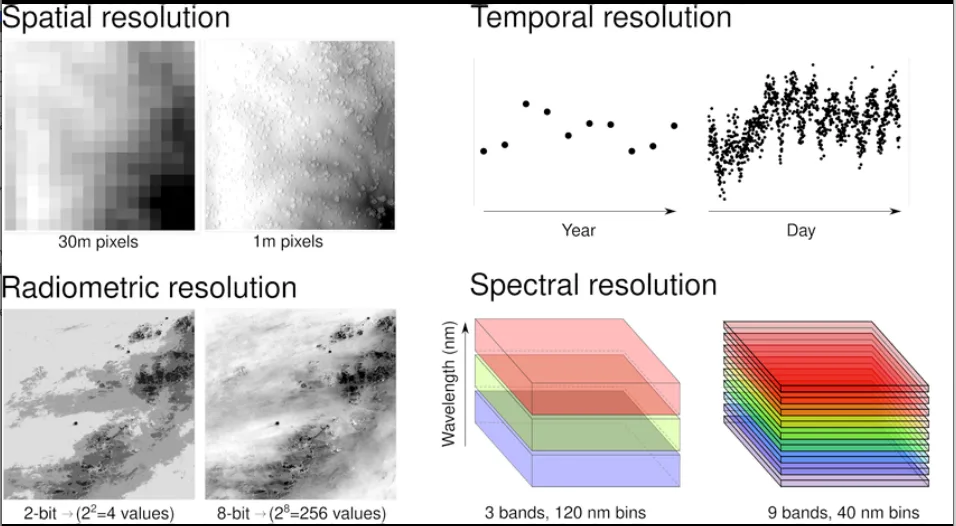
Spatial Resolution
Refers to the smallest object that can be detected in an image.
Radiometric Resolution
Defines the sensor’s ability to detect small differences in energy.
Temporal Resolution
Indicates how frequently images of the same area can be captured.
Spectral Resolution
Refers to the range of electromagnetic wavelengths a sensor can detect.
Properties of Spherical Triangles
- Sum of angles is greater than 180° and less than 540°
- Each side is less than 180°
- Spherical triangles are used in geodetic surveying
Traverse and Tacheometry Concepts
Traverse Method
- The axis method is used when distances are measured very accurately
- In tacheometry, the staff intercept remains constant
- Baseline should be as long as possible for better accuracy
Angular Error of Closure
Angular error depends on:
- Number of sides
- Least count of the instrument
Methods of Locating Ground Points
Indirect Methods
- Chain and compass method
- Tacheometric method
- Square method
Direct Method
- Vertical control method
EDM (Electronic Distance Measurement) Instruments
- EDM instruments require only one station
- Intermediate stations are not required
- The radar antenna sends microwave signals to the target
Differences Between IS 1893:2016 and IS 1893:2025 for Earthquake Resistant Design:- https://engineerlatest.com/differences-between-is-18932016-and-is-18932025-for-earthquake-resistant-design/
Understanding the Overstrength Factor in Structural Engineering | IS 1893: 2025 Guide:- https://engineerlatest.com/nderstanding-overstrength-factor-structural-design/










2 comments