Aravali Forest Degradation: Environmental Impact and Urban Development Challenges
Table of Contents
The Aravali range is one of the oldest mountain systems in the world and plays a silent but critical role in North India’s environmental balance. Stretching across Rajasthan, Haryana, and parts of Delhi, the Aravali forests act as a natural barrier against desertification, air pollution, and groundwater depletion.
In recent years, concerns have increased regarding the gradual degradation of the Aravali region due to urban expansion, infrastructure development, and human activities. This article explains the issue from an environmental and engineering perspective, without blame or sensationalism—only facts, impacts, and solutions.
Why the Aravali Range Is Environmentally Important
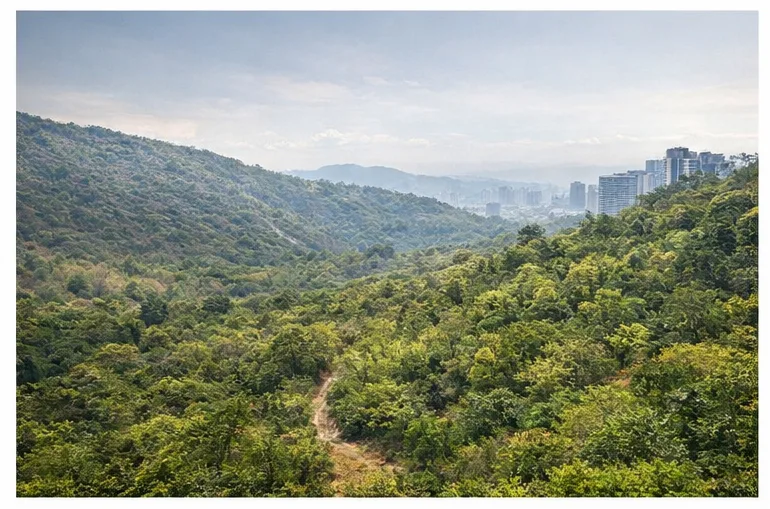

The Aravali hills are much more than just rocky terrain. They provide several ecological services that directly affect millions of people.
1. Natural Barrier Against Desert Expansion
The Aravali range prevents the Thar Desert from spreading eastward. Loss of vegetation in this region increases the risk of desertification in Haryana, Delhi, and western Uttar Pradesh.
2. Air Pollution Control
Aravali forests act as a green lung for NCR. Trees trap dust particles and reduce wind-borne pollution. Degradation of forest cover weakens this natural filtration system, contributing to higher AQI levels.
3. Groundwater Recharge
The rocky and fractured geology of the Aravali allows rainwater to percolate and recharge aquifers. Deforestation and surface sealing reduce infiltration, leading to falling groundwater levels.
Current Development Pressure on the Aravali Region

Rapid urbanization and infrastructure demand have increased pressure on land resources near growing cities. Expansion of roads, housing, industrial zones, and utilities often overlaps with ecologically sensitive areas.
From a planning perspective, the challenge is not development itself, but unplanned and poorly regulated development.
Key concerns include:
- Loss of native vegetation
- Increased soil erosion
- Disturbance of natural drainage patterns
- Heat island effect due to concrete surfaces
Environmental Impact of Forest Degradation in Aravali

1. Rising Air Pollution in NCR
Multiple studies indicate that a reduction in green cover around Delhi worsens dust storms and smog conditions, especially during dry seasons.
2. Water Scarcity
Reduced forest cover means:
- Less rainwater absorption
- Faster surface runoff
- Lower groundwater recharge
This directly affects water availability for urban and rural populations.
3. Biodiversity Loss
Aravali forests support diverse plant and animal species. Habitat fragmentation threatens local biodiversity and disrupts ecological balance.
Engineering and Urban Planning Challenges
From an engineering standpoint, development in sensitive regions like the Aravali requires careful planning and environmental integration.
Common challenges include:
- Designing infrastructure without disturbing natural slopes
- Managing stormwater runoff
- Preventing soil erosion
- Balancing construction needs with environmental safeguards
Ignoring these factors can lead to:
- Flooding during heavy rainfall
- Structural instability
- Long-term environmental damage
Role of Sustainable Development and Engineering Solutions
Development and environmental protection do not have to be opposing forces. With the right approach, both can coexist.
Sustainable solutions include:
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) before projects
- Preserving natural drainage channels
- Green buffer zones around construction
- Use of permeable pavements
- Large-scale afforestation and restoration projects
Engineers, planners, and policymakers play a key role in ensuring responsible development.
Importance of Policy and Awareness

Environmental regulations exist to protect ecologically sensitive zones, but their effectiveness depends on:
- Scientific assessment
- Transparent implementation
- Public awareness
Long-term sustainability requires collaboration between government bodies, professionals, and communities.
The Aravali range is not just a forested region—it is a life-support system for North India. Its degradation affects air quality, water availability, climate resilience, and overall environmental health.
The real solution lies in balanced development, where infrastructure growth respects natural systems instead of replacing them. By adopting sustainable planning, scientific engineering practices, and environmental awareness, it is possible to protect the Aravali while meeting development needs.
Protecting the Aravali today is an investment in clean air, water security, and climate stability for future generations.
This article is written for educational and informational purposes and does not intend to accuse or target any individual, organization, or authority.
Aravali Forest Degradation
Earthquake-Resistant Building Design in India: What Really Matters on Site:- https://engineerlatest.com/earthquake-resistant-building-design-india/











Post Comment